Chromium, cobalt, vanadium and manganese chemistry
COBALT
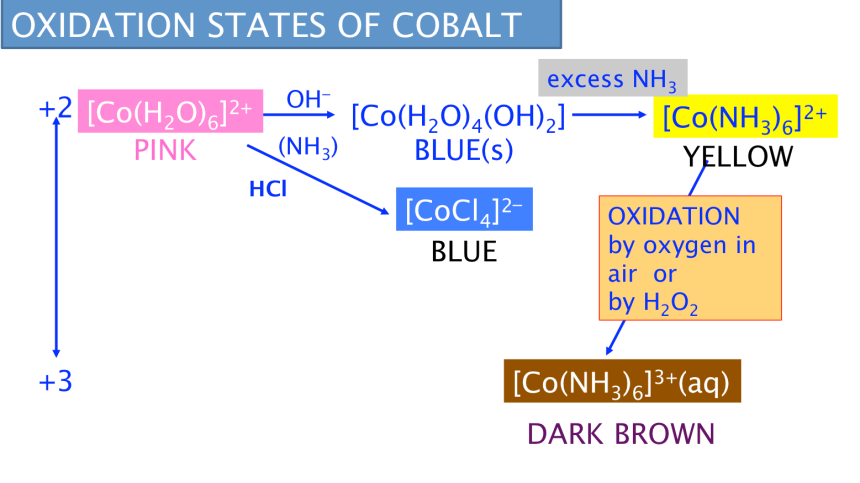
Cobalt exists in two stable oxidation states, +2 and +3.
Acidic or neutral solutions: [Co(H2O)6]2+ pink
Alkaline solution: [Co(H2O)4(OH)2] blue (s)
Oxidation of Co2+ by air or H2O2 in ammoniacal solution through a sequence of reactions:
1. Ammonia acting as a base:
[Co(H2O)6]2+ + 2OH− → [Co(H2O)4(OH)2] + 2H2O
[Co(H2O)6]2+ + 2NH3 → [Co(H2O)4(OH)2] +2NH4+
(pink solution) (blue (s))
2. Ligand exchange reaction (excess NH3):
[Co(H2O)4(OH)2] + 6NH3 → [Co(NH3)6]2+ + 2OH− + 4H2O
(blue (s)) (yellow/straw solution)
3. Oxidation reaction ( by oxygen in air or by H2O2):
Utilising the following half-equations for the oxidising agent:
O2 + 2H2O + 4e− → 4OH−
H2O2 + 2e− → 2OH−
4[Co(NH3)6]2+ + O2 + 2H2O → 4[Co(NH3)6]3+ + 4OH−
(yellow/straw solution) (dark brown solution)
2[Co(NH3)6]2+ + H2O2 → 2[Co(NH3)6]3+ + 2OH−
(yellow/straw solution) (dark brown solution)
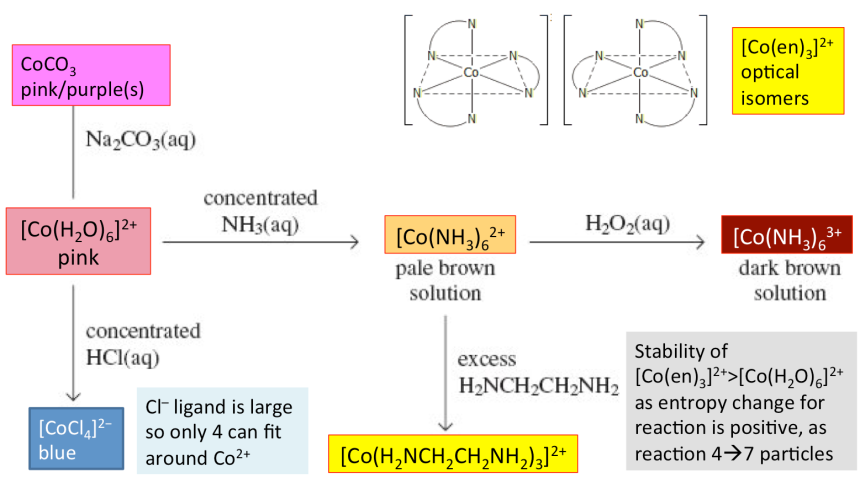
- Similarly, ethane-1,2-diamine may be complexed with Co2+ and oxidised by oxygen in air to Co3+ complex.
4[Co(H2NCH2CH2NH2)3]2+ + O2 + 2H2O → 4[Co(H2NCH2CH2NH2)3]3+ + 4OH−
Ligand substitution with HCl
[Co(H2O)6]2+ + 4Cl− ⇌ [CoCl4]2− + 6H2O ΔH +ve (endothermic)
(pink solution) (blue solution)
The larger sized chloride ion ligand leads to a change in coordination number, complex shape (octahedral to tetrahedral), colour, and cationic to anionic form, without any change in oxidation state.
In accordance with Le Chatelier’s principle, dilution and/or cooling the blue complex shifts the equilibrium position to the left, promoting formation of the pink complex.
Oxidation of Iodide by [Co(H2O)6]3+
2[Co(H2O)6]3+ + 2I− ⇌ 2[Co(H2O)6]2+ + I2
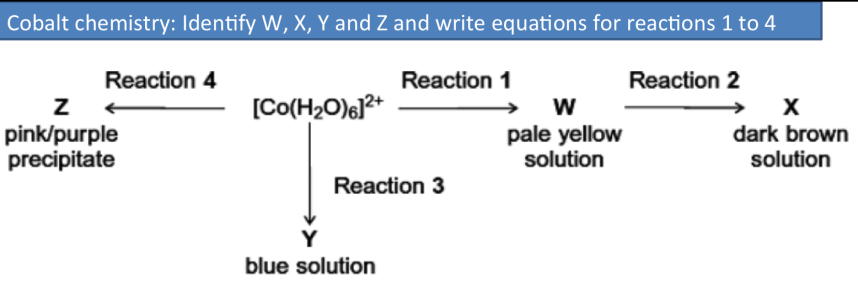
Summary of key reaction pathways for cobalt
[Co(NH3)6]2+ + CO32− → CoCO3 + 6H2O
(pink solution) (purple/pink solid)
[Co(H2O)6]2+ + 6NH3 → [Co(NH3)6]2+ + 6H2O
(pink solution) (yellow/straw solution)
2[Co(NH3)6]2+ +H2O2 → 2[Co(NH3)6]3+ + 2OH−
(yellow/straw solution) (dark brown solution)
Let en represent the bidentate ethane-1,2-diamine ligand (H2NCH2CH2NH2)
[Co(NH3)6]2+ + 3en [Co(en)3]2+ + 6NH3
(yellow/straw solution) (yellow/orange solution)
[Co(H2O)6]2+ + 4Cl− ⇌ [CoCl4]2− + 6H2O
(pink solution) (blue solution)
Reaction 1 uses reagent NH3: [Co(H2O)6]2+ + 6NH3 → [Co(NH3)6]2+ + 6H2O
Reaction 2 uses reagent H2O2: 2[Co(NH3)6]2+ + H2O2 → 2[Co(NH3)6]3+ + 2OH−
Reaction 3 uses reagent HCl: [Co(H2O)6]2+ + 4HCl → [CoCl4]2− + 6H2O + 4H+
Reaction 4 uses reagent Na2CO3: [Co(H2O)6]2+ + CO32− → CoCO3 + 6H2O